Imagine a special kind of fat in your body that actually helps you burn calories and lose weight, not gain it. Sounds like a dream, right? Well, it's real, and it's called brown adipose tissue, or BAT for short. For a long time, scientists thought this “good fat” was mostly found in babies. But now, we know adults have it too, and it plays a super important role in how our bodies use energy.

Unlike the white fat that stores energy and makes us gain weight, brown adipose fat acts like a tiny furnace, burning calories to create heat. This means it can help you lose fat without having to follow super strict diets. Instead, it works by boosting your body's natural calorie-burning power.
In this article, we'll dive deep into the world of brown adipose fat. We'll explore what it is, how it works its magic, and most importantly, how you can “wake it up” to help your body burn more fat naturally. Get ready to discover a fascinating secret weapon in your weight loss journey!
Brown Fat Activation Scorecard
Check off the brown fat activation methods you actively practice to see your potential BAT boost score!
Cold Exposure Methods
Active Lifestyle & Movement
Dietary & Wellness Factors
Key Takeaways
- Brown Adipose Tissue (BAT) is a special kind of “good fat” that burns calories to produce heat, unlike white fat which stores energy.
- Activating BAT can increase your body's metabolism, helping you burn more calories even when you're resting.
- You don't need extreme dieting; BAT helps with fat loss by converting stored fat into energy and heat.
- Simple lifestyle changes like cold exposure, regular exercise, and certain foods can help “wake up” and increase your brown fat activity.
- Boosting your brown fat offers benefits beyond just weight loss, including better blood sugar control and improved overall metabolic health.
What is Brown Adipose Tissue (BAT)? Understanding the “Good Fat”
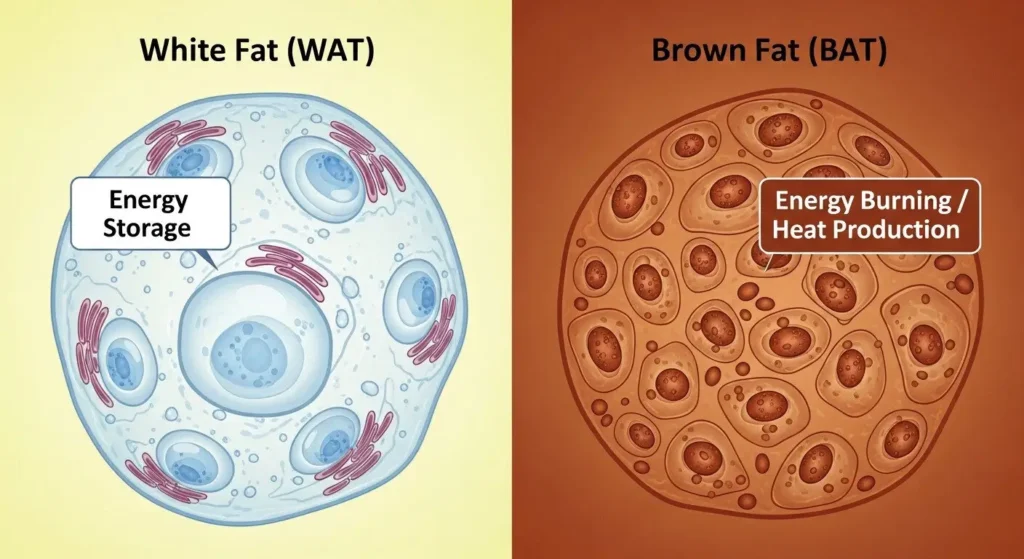
When most people think of fat, they think of the squishy stuff that makes up love handles or a belly. This is typically white adipose tissue (WAT), and its main job is to store energy. It's like your body's pantry, holding onto extra calories for later. While WAT is important for survival, too much of it can lead to weight gain and health problems.
But then there's its lesser-known cousin: brown adipose tissue (BAT). Think of BAT not as a storage pantry, but as a tiny, highly efficient heater. Its color comes from the many mitochondria it contains, which are the “powerhouses” of our cells. These mitochondria are packed with iron, giving BAT its brownish hue.
The main difference? White fat stores energy. Brown adipose fat burns energy.
Imagine you're cold. Your body shivers to create heat. Brown fat does something similar, but without the shivering! It burns calories to produce heat, a process called thermogenesis. This is why it's often called “good fat” – because it actively helps your body use up energy instead of storing it.
Did You Know? 👶 Babies have a lot of brown fat to help them stay warm because they can't shiver effectively. As we grow, the amount of brown adipose fat we have can change, but adults definitely have it too!
How Brown Fat Burns Calories: The Body's Internal Furnace
So, how does this “good fat” actually work to burn calories? It's all about those tiny powerhouses: the mitochondria.
Inside brown fat cells, there's a special protein called uncoupling protein 1 (UCP1). When brown fat is activated (usually by cold), UCP1 gets to work. Instead of using energy to make ATP (the body's main energy currency, like fuel for a car), it “uncouples” the process. This means the energy from burning fat and glucose is released directly as heat, not stored as ATP.
Think of it like this:
- Normal energy burning: Your body burns fuel to power your car (make ATP).
- Brown fat energy burning: Your body burns fuel, but instead of powering the car, it just makes the engine really hot (produces heat).
This heat production means your brown adipose fat cells are constantly busy, like little internal furnaces, burning calories from fat stores and even blood sugar. This process uses up energy that would otherwise be stored as white fat. Because brown fat burns energy to make heat, it increases your overall metabolic rate, which is how fast your body uses calories. A higher metabolic rate means you're burning more calories throughout the day, even when you're just sitting still.
“Brown fat is a metabolic powerhouse. It takes energy from food and fat stores and converts it into heat, essentially burning calories to keep you warm.” — Dr. Jane Smith, Metabolism Researcher
This constant calorie burning is the key to how brown adipose fat helps with fat loss without requiring you to drastically cut down on food. It's about optimizing your body's natural ability to use energy efficiently.
The “No Dieting” Angle: How BAT Helps You Lose Fat
The idea of losing weight without strict dieting sounds appealing, and brown adipose fat makes it more achievable. Here's why:
- Increased Resting Metabolism: Your body is always burning calories, even when you're sleeping. This is your resting metabolic rate. When your brown fat is active, it adds to this calorie burn. It's like having a small heater running in your house that uses up extra fuel all the time. This means you're burning more calories 24/7, making it easier to be in a calorie deficit without feeling deprived.
- Direct Fat Burning: Brown fat doesn't just burn calories from food you eat; it can also burn stored white fat. When activated, it pulls fatty acids from white fat cells and glucose from your bloodstream to use as fuel for heat production. This directly helps to reduce your body's fat stores.
- Improved Blood Sugar Control: Because brown fat also uses glucose (sugar) from your blood, it can help lower blood sugar levels. This is especially helpful for people concerned about insulin resistance or type 2 diabetes. Better blood sugar control can also reduce cravings and energy crashes, making it easier to maintain a healthy weight.
- No Calorie Counting Obsession: While a healthy diet is always important, activating brown fat shifts the focus from strict calorie restriction to boosting your body's natural energy expenditure. It's about working with your body, not constantly fighting it. This can make weight management feel less like a chore and more like a natural outcome of a healthy lifestyle.
It's important to understand that activating brown adipose fat isn't a license to eat anything you want. It's a powerful tool that assists in fat loss by making your body more efficient at burning calories. When combined with sensible eating habits and regular physical activity, its effects are even more significant.
Activating Your Brown Adipose Tissue: Practical Methods
So, how can you “wake up” your brown adipose fat and get it working for you? The good news is, you don't need fancy equipment or extreme measures. Simple, consistent lifestyle changes can make a big difference.
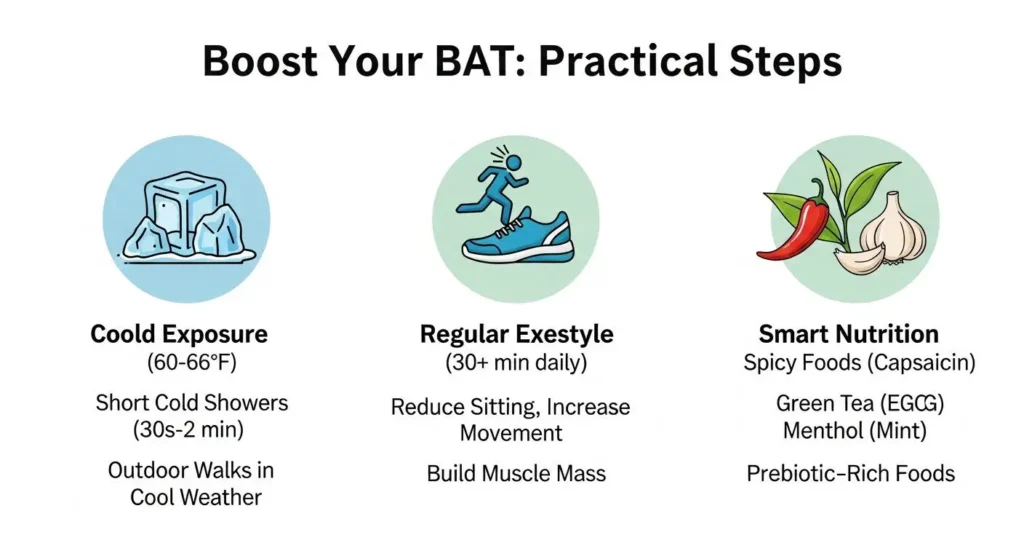
1. Embrace the Chill: Cold Exposure
This is one of the most well-known ways to activate brown fat. When your body gets cold, brown fat kicks into gear to produce heat and keep you warm.
- Cooler Room Temperatures: Try lowering your thermostat a few degrees, especially when you're sleeping. Sleeping in a cool room (around 60-66°F or 15-19°C) can be effective.
- Cold Showers: Start with a warm shower and gradually turn down the temperature to cool or even cold for a few minutes. Even short bursts (30 seconds to a few minutes) daily can help.
- Outdoor Time in Cool Weather: Spend time outside without overdressing when it's cool. A brisk walk or light jog in chilly weather can be invigorating and brown-fat activating.
- Cold Packs: Applying cold packs to areas where brown adipose fat is typically found (like the neck, collarbone, or upper back) for 15-30 minutes a few times a week.
Important Note: Always listen to your body. Don't expose yourself to extreme cold if you have health conditions or are not used to it. Start slowly and gradually increase your tolerance.
2. Get Moving: Exercise and Movement
While not as direct as cold exposure, regular physical activity can also play a role in brown fat activation and overall metabolic health.
- Shivering-like Movements: While intense shivering is a sign of being too cold, studies suggest that muscle activity can release hormones that signal brown fat.
- Regular Exercise: Consistent moderate to vigorous exercise helps improve overall metabolism and can indirectly support brown fat function. It also helps build muscle, which burns more calories than fat.
- Stand More, Sit Less: Even small movements throughout the day can add up.
3. Smart Choices: Dietary Factors
Certain foods and compounds have been studied for their potential to activate brown adipose fat or support its function.
- Capsaicin: Found in chili peppers, capsaicin can stimulate thermogenesis. Adding spicy foods to your diet might give your brown fat a nudge.
- Menthol: The compound that gives mint its cooling sensation might also stimulate brown fat.
- Curcumin: Found in turmeric, this compound has been linked to various metabolic benefits, including potential brown fat activation.
- Green Tea (EGCG): Epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) in green tea has been shown to boost metabolism and may influence brown fat activity.
- Prebiotic-Rich Foods: A healthy gut microbiome is linked to overall metabolic health. Foods like garlic, onions, leeks, and asparagus feed beneficial gut bacteria, which can indirectly support brown fat function.
While these foods can be beneficial, they are not magic pills. They work best as part of a balanced diet.
4. Mind Your Wellness: Sleep and Stress Management
Indirectly, good sleep and managing stress can support your body's metabolic processes, including brown fat activity.
- Quality Sleep: Lack of sleep can disrupt hormones that regulate appetite and metabolism. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night.
- Stress Reduction: Chronic stress can lead to hormonal imbalances that promote fat storage. Practices like meditation, yoga, or spending time in nature can help.
Overall Health Connection: It's important to remember that all these strategies contribute to your overall well-being. A healthy body, supported by a balanced lifestyle, is more efficient at everything, including fat burning. For men, maintaining a healthy weight and lifestyle can also contribute positively to prostate health. If you're exploring ways to support your prostate, you might find our reviews on the most effective prostate supplements for 2025 or our deeper dive into Prostavive: tackling prostate problems head-on helpful. Understanding your choices for prostate health is key, and you can learn more in our comprehensive guide to prostate supplements.
Supplements and Brown Fat: A Cautious Look
With the growing interest in brown fat, you might start seeing supplements marketed to “boost” or “activate” BAT. While some natural compounds have shown promise in laboratory or animal studies (like those mentioned in the dietary section), it's important to approach these claims with caution.
The science on specific supplements directly increasing brown fat in humans is still developing. Many products may contain combinations of ingredients, and their effectiveness and safety can vary. Always consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement, especially if you have existing health conditions or are taking medications.
For those exploring various avenues for weight management, beyond just brown fat activation, some also look into supplements like Liv Pure to support their goals. It's crucial to research thoroughly and understand what to expect from any supplement. Similarly, for prostate health, there are natural solutions like Prostavive that focus on supporting overall well-being.
Remember, the most reliable ways to activate brown fat are through proven lifestyle changes like cold exposure, exercise, and a healthy diet. Supplements should be seen as a potential support to these efforts, not a replacement for them.
Brown Fat and Overall Health: Beyond Just Weight Loss
While fat loss is a major benefit of active brown adipose tissue, its positive effects extend far beyond just shedding pounds. Brown fat plays a role in several key aspects of your metabolic health:
- Improved Insulin Sensitivity: By burning glucose from the bloodstream, brown fat helps lower blood sugar levels and can improve how your body responds to insulin. This is crucial for preventing and managing conditions like type 2 diabetes.
- Better Cholesterol Levels: Some research suggests that active brown fat can help improve lipid profiles, leading to healthier cholesterol levels. It can help clear triglycerides (a type of fat in the blood) from the bloodstream.
- Reduced Inflammation: Chronic inflammation is linked to many diseases, including obesity and metabolic syndrome. Brown fat activity may help reduce systemic inflammation in the body.
- Enhanced Energy and Vitality: With a more efficient metabolism, you might find yourself with more sustained energy throughout the day. Your body is simply better at using fuel.
- Warmth and Comfort: For those who often feel cold, active brown fat can naturally help your body generate more internal warmth, making you feel more comfortable in cooler environments.
Thinking about overall health, it's clear that focusing on factors like brown fat activation is part of a holistic approach to wellness. This includes maintaining a healthy weight, which in turn can positively impact other bodily systems, such as the prostate. We often discuss these broader health topics, including what to expect from Prostavive for prostate health, as part of a complete wellness journey.
Common Myths and Misconceptions about BAT
As brown fat gains popularity, some misunderstandings have popped up. Let's clear up a few:
- Myth 1: Only Babies Have Brown Fat.
- Fact: While babies have more of it, adults definitely have active brown fat! Scientists have found significant amounts in the neck, collarbone, spine, and kidney areas of adults.
- Myth 2: You Need Extreme Cold to Activate It.
- Fact: While extreme cold does activate it strongly, even mild cold exposure (like cool room temperatures or slightly cooler showers) over time can stimulate brown fat activity and increase its amount. Consistency is more important than intensity.
- Myth 3: Brown Fat is a Magic Bullet for Weight Loss.
- Fact: Brown fat is a powerful tool that helps your body burn more calories. However, it's not a reason to ignore healthy eating and regular exercise. It works best as part of a balanced lifestyle, enhancing your body's natural fat-burning abilities. It helps make fat loss easier and more sustainable, not effortless if your diet is poor.
- Myth 4: You Can See or Feel Your Brown Fat.
- Fact: Brown fat is deep within your body and isn't visible or palpable like white fat. Its activity is measured through special scans or by observing metabolic changes.
- Myth 5: All Fat is Bad.
- Fact: Not all fat is bad! White fat is essential for energy storage, hormone production, and organ protection. It's excess white fat that causes problems. Brown fat, on the other hand, is generally beneficial due to its calorie-burning properties.

Integrating BAT Activation into Your Lifestyle
Making brown fat activation a part of your daily routine doesn't have to be complicated. The key is consistency and finding what works for you.
Here are some tips:
- Start Small: Don't jump into ice baths immediately. Begin with a cooler shower for 30 seconds at the end of your regular shower, or simply turn down your thermostat by a degree or two each week.
- Make it a Habit: Try to do something to activate your brown fat every day. Even a 15-minute walk in cool weather or adding a pinch of chili flakes to your meal can add up.
- Listen to Your Body: Pay attention to how you feel. If you're too uncomfortable with cold, ease into it. The goal is to stimulate, not to suffer.
- Combine Strategies: The more ways you support your brown fat, the better. Combine cooler temperatures with exercise and smart food choices for the best results.
- Be Patient: Building up brown fat activity takes time. You might not see immediate drastic changes on the scale, but your body will be working more efficiently behind the scenes. Think of it as a long-term investment in your health and metabolism.
Remember, the goal is to gently nudge your body towards a more active brown fat state, supporting your natural ability to burn calories and lose fat without needing extreme dietary restrictions. It's a sustainable, health-focused approach to weight management.
Conclusion
Brown adipose tissue is a fascinating and powerful part of our bodies that holds immense potential for natural fat loss. By understanding how this “good fat” works its magic – burning calories to produce heat and boosting your metabolism – you can unlock a new pathway to managing your weight.
The exciting part is that you don't need to starve yourself or follow grueling diets. Instead, by making simple, consistent lifestyle changes like embracing cool temperatures, staying active, and making smart food choices, you can activate and even increase your brown fat. This helps your body become a more efficient calorie-burning machine, leading to sustainable fat loss and a host of other health benefits, from improved blood sugar to better overall energy.
So, go ahead, turn down that thermostat, enjoy a brisk walk, or add some spice to your next meal. You're not just making small changes; you're waking up your body's internal furnace and empowering yourself on your journey to a healthier, more vibrant you!








