Keeping your normal blood sugar reading in a healthy range is super important for your overall health, energy, and even your mood. Think of blood sugar, or glucose, as the main fuel for your body's cells. When these levels are too high or too low for too long, it can lead to serious health problems.

But don't worry! Achieving a normal blood sugar reading daily is more achievable than you might think. This guide will break down simple, effective strategies you can use every day to keep your blood sugar balanced and feel your best.
Key Takeaways
- Understand Your Numbers: Knowing what a normal blood sugar reading looks like and regularly checking your levels helps you make smart choices.
- Eat Smart, Not Less: Focus on balanced meals with lean protein, healthy fats, and complex carbohydrates to keep blood sugar steady.
- Move Your Body: Regular physical activity, both cardio and strength training, helps your body use glucose better and lowers blood sugar.
- Manage Stress & Sleep Well: Stress and lack of sleep can raise blood sugar. Finding ways to relax and getting enough rest are crucial.
- Stay Consistent: Small, daily habits add up to big results. Consistency in diet, exercise, and monitoring is key to long-term success.
What is Blood Sugar and Why Does It Matter?
Blood sugar, or glucose, is a type of sugar that comes from the food you eat. It's your body's main source of energy. Your blood carries glucose to all your cells, and a hormone called insulin helps your cells take in this glucose.
When you eat, your blood sugar levels go up. Your pancreas then releases insulin to bring those levels back down. If this system isn't working right, your blood sugar can stay too high (hyperglycemia) or drop too low (hypoglycemia). Both can be harmful.
Why is a normal blood sugar reading so important? Keeping your blood sugar stable helps:
- Maintain steady energy levels throughout the day.
- Improve your mood and concentration.
- Protect your organs (like your heart, kidneys, and eyes) from damage over time.
- Reduce your risk of developing type 2 diabetes and other health complications.
What's a “Normal” Blood Sugar Reading?
Understanding what numbers are considered healthy is the first step. Here's a quick look at typical target ranges for most adults, though your doctor might give you slightly different goals:
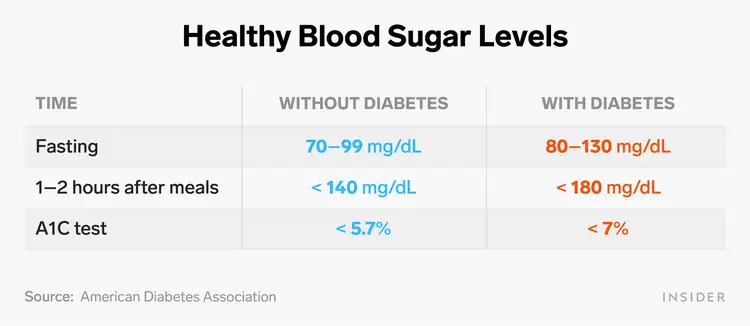
| When You Check | Normal Range (mg/dL) | Normal Range (mmol/L) |
|---|---|---|
| Fasting (after 8+ hours without food) | 70-99 | 3.9-5.5 |
| Before a Meal | 70-130 | 3.9-7.2 |
| 1-2 Hours After a Meal | Less than 140 | Less than 7.8 |
| A1C Test (average over 2-3 months) | Below 5.7% |
Always discuss your specific target ranges with your healthcare provider.
The Role of Diet in Blood Sugar Control
What you eat has the biggest impact on your blood sugar levels. Making smart food choices is a cornerstone of achieving a normal blood sugar reading daily. It's not about cutting out all your favorite foods, but rather understanding how different foods affect your body and making balanced choices.
Carbohydrates: The Main Event
Carbohydrates are the primary source of glucose. But not all carbs are created equal!
- Simple Carbs: Found in sugary drinks, candies, white bread, and processed snacks. They cause quick, high spikes in blood sugar because they're digested very fast.
- Complex Carbs: Found in whole grains (oats, brown rice, quinoa), vegetables, and legumes. They are digested slowly, providing a steady release of glucose and preventing sharp spikes. Choose these more often!
Tip: Focus on the quality of your carbs. Think whole, unprocessed foods.
Fiber: Your Blood Sugar's Best Friend
Fiber is a type of carbohydrate that your body can't digest. It's incredibly helpful for blood sugar control because it:
- Slows sugar absorption: This prevents rapid blood sugar spikes after meals.
- Improves insulin sensitivity: Helps your body use insulin more effectively.
- Keeps you full: Aids in weight management, which is beneficial for blood sugar.
Where to find fiber:
- Vegetables: Broccoli, spinach, carrots, bell peppers
- Fruits: Berries, apples (with skin), pears, oranges
- Legumes: Lentils, beans, chickpeas
- Whole Grains: Oats, whole-wheat bread, brown rice
Protein and Healthy Fats: The Stabilizers
Adding lean protein and healthy fats to your meals can significantly help stabilize blood sugar. They slow down digestion, which means glucose enters your bloodstream more gradually.
Good sources of protein:
- Chicken, turkey, fish
- Eggs
- Tofu, tempeh
- Greek yogurt, cottage cheese
- Nuts and seeds
Healthy fats to include:
- Avocado
- Olive oil, avocado oil
- Nuts and seeds
- Fatty fish (salmon, mackerel)
Pull Quote: “Eating a balanced plate with fiber-rich carbs, lean protein, and healthy fats is like building a strong dam against blood sugar floods. It keeps things steady and controlled.”
Meal Timing and Portion Control
It's not just what you eat, but when and how much.
- Regular Meals: Aim for consistent meal times. Skipping meals can lead to overeating later or cause blood sugar to drop too low, followed by a rebound high.
- Smaller, More Frequent Meals: Some people find that eating smaller, more frequent meals (e.g., three main meals and two healthy snacks) helps keep blood sugar more stable throughout the day.
- Portion Sizes: Be mindful of how much you're eating, especially carbohydrates. Even healthy carbs can raise blood sugar if consumed in large amounts.
Hydration: Don't Forget Water!
Drinking enough water is a simple yet powerful way to support healthy blood sugar. Water helps your kidneys flush out excess sugar through urine. Dehydration can lead to higher blood sugar concentrations. Aim for at least 8 glasses of water daily.
For those looking to manage their weight, which often goes hand-in-hand with blood sugar control, exploring options like Liv Pure reviews can provide insights into supporting liver health and fat-burning processes, which can indirectly contribute to better glucose metabolism.
The Power of Physical Activity
Regular physical activity is an incredibly effective tool for managing blood sugar and achieving a normal blood sugar reading. When you exercise, your muscles use glucose for energy, which helps lower the sugar in your bloodstream. It also makes your body more sensitive to insulin, meaning your cells can take in glucose more efficiently.

Types of Exercise to Consider
- Aerobic Exercise (Cardio): Activities that get your heart rate up and make you breathe harder.
- Examples: Brisk walking, jogging, swimming, cycling, dancing.
- Benefits: Directly lowers blood sugar during and after your workout.
- Goal: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity per week (e.g., 30 minutes, 5 days a week).
- Strength Training (Resistance Training): Activities that build muscle mass.
- Examples: Lifting weights, using resistance bands, bodyweight exercises (push-ups, squats, lunges).
- Benefits: More muscle means more places for your body to store glucose, even when you're not exercising. This improves long-term blood sugar control.
- Goal: Aim for 2-3 sessions per week on non-consecutive days.
Consistency is Key! The most important thing is to find activities you enjoy and stick with them. Even short bursts of activity throughout the day, like a 10-minute walk after meals, can make a difference. Start slow and gradually increase the intensity and duration. Always consult your doctor before starting any new exercise program, especially if you have existing health conditions.
Stress Management and Sleep
You might be surprised to learn how much your mind and rest affect your blood sugar. Stress and lack of sleep can throw your blood sugar levels out of whack, making it harder to get a normal blood sugar reading.
How Stress Affects Blood Sugar
When you're stressed, your body releases hormones like cortisol and adrenaline. These hormones are part of your “fight or flight” response, and they tell your body to release stored glucose for quick energy. This can lead to a rise in blood sugar, even if you haven't eaten anything. Chronic stress means your blood sugar can stay elevated for longer periods.
Ways to manage stress:
- Mindfulness and Meditation: Even a few minutes a day can help calm your nervous system.
- Deep Breathing Exercises: Simple and effective for immediate stress relief.
- Yoga or Tai Chi: Combine physical movement with relaxation.
- Hobbies and Relaxation: Engage in activities you enjoy, like reading, listening to music, or spending time in nature. 🧘♀️
- Social Connection: Spend time with loved ones.

The Importance of Sleep
Poor sleep can significantly impact your blood sugar. When you don't get enough sleep, your body becomes less sensitive to insulin, meaning it has a harder time moving glucose from your blood into your cells. Lack of sleep also increases stress hormones and can make you crave sugary, high-carb foods.
Tips for better sleep:
- Stick to a Schedule: Go to bed and wake up around the same time every day, even on weekends.
- Create a Relaxing Bedtime Routine: A warm bath, reading a book, or gentle stretching.
- Make Your Bedroom Sleep-Friendly: Dark, quiet, and cool.
- Limit Screen Time: Avoid phones, tablets, and computers an hour before bed.
- Avoid Caffeine and Heavy Meals Before Bed: These can interfere with sleep.
Monitoring Your Blood Sugar
Regularly checking your blood sugar is a powerful way to understand how different foods, activities, and stress levels affect you. It's like having a personal coach telling you what's working and what's not, helping you achieve a normal blood sugar reading consistently.
Why Monitor?
- See Patterns: You can identify trends and learn how your body responds to various situations.
- Make Informed Choices: If a certain food causes a spike, you know to adjust next time.
- Track Progress: See the positive impact of your lifestyle changes.
- Prevent Complications: Catch high or low readings before they become serious problems.
How to Monitor
- Blood Glucose Meter (Glucometer): This is a small, portable device that measures the amount of glucose in a drop of blood from your fingertip.
- When to check: Your doctor will advise you, but common times are fasting (first thing in the morning), before meals, and 1-2 hours after meals.
- Keep a Log: Write down your readings, along with what you ate, your activity level, and any symptoms. This helps you and your doctor spot patterns.
- Continuous Glucose Monitor (CGM): A CGM is a small sensor worn on your skin (usually on the arm or belly) that automatically measures glucose levels every few minutes, day and night. It sends the readings to a receiver or smartphone app.
- Benefits: Provides a more complete picture of your blood sugar trends, including how levels change during sleep or between meals. It can also alert you to highs and lows.
- Availability: CGMs are often prescribed for people with diabetes, but some individuals without diabetes use them for better insight into their metabolism and to help maintain a normal blood sugar reading. Discuss with your doctor if a CGM is right for you.
Pull Quote: “Knowledge is power when it comes to your blood sugar. Regular monitoring helps you see what works best for your body, empowering you to make the right choices for a normal blood sugar reading.”
Medication and Supplements: A Holistic Approach
While diet, exercise, stress management, and sleep are the cornerstones of maintaining a normal blood sugar reading, sometimes medication or supplements may play a role. It's crucial to remember that any discussion about medication or supplements should always be had with your healthcare provider. They can help you understand what's appropriate for your individual health needs.
Prescription Medications
For individuals with prediabetes or diabetes, doctors might prescribe medications to help manage blood sugar. These can include:
- Metformin: Often a first-line medication for type 2 diabetes, it helps reduce glucose production by the liver and improves insulin sensitivity.
- Sulfonylureas or Meglitinides: These medications stimulate the pancreas to release more insulin.
- SGLT2 Inhibitors: Help the kidneys remove more glucose from the body through urine.
- GLP-1 Receptor Agonists: Slow digestion and increase insulin release.
These medications are powerful tools, but they work best when combined with healthy lifestyle changes.
The Role of Supplements
Many people explore supplements to support their overall health, including blood sugar management. Some supplements are marketed for blood sugar control, such as chromium, cinnamon, berberine, or alpha-lipoic acid.
- Important Note: The effectiveness of many supplements for blood sugar control is not always strongly supported by scientific research, and they are not regulated as strictly as medications.
- Always Consult Your Doctor: Before taking any supplement, talk to your healthcare provider. Some supplements can interact with medications or have side effects.
When considering a holistic view of your health, it's worth noting that different areas of the body are interconnected. For men, addressing specific health concerns like prostate health can be part of an integrated wellness approach. For example, you might want to learn about the most effective prostate supplements reviewed for 2025 or explore how to start tackling prostate problems head-on. Understanding all aspects of your health is vital, just as you learn about blood sugar. A comprehensive guide to prostate supplements can help you make informed decisions about men's health. Similarly, exploring a natural solution for prostate health might be part of a broader wellness plan that also supports stable blood sugar.
The key is to view your health as a whole, ensuring that all aspects are supported, whether through diet, exercise, or, if necessary, carefully chosen medications and supplements under medical guidance.
Lifestyle Habits for Long-Term Success
Keeping a normal blood sugar reading daily isn't a one-time fix; it's a journey of consistent healthy habits. Building a sustainable lifestyle is crucial for long-term success.
Consistency is Your Best Friend
- Routine: Try to eat meals at similar times, exercise regularly, and maintain a consistent sleep schedule. Your body loves routine!
- Small Steps: Don't try to change everything at once. Pick one or two habits to focus on, master them, and then add more. Small, consistent changes are easier to maintain than drastic overhauls.
- Patience: It takes time to see results and for your body to adapt. Be patient and kind to yourself.
Regular Check-ups and Professional Guidance
- Doctor's Visits: Schedule regular appointments with your doctor to monitor your blood sugar, A1C, and overall health. They can adjust your treatment plan as needed.
- Dietitian/Nutritionist: A registered dietitian can provide personalized meal plans and advice tailored to your specific needs and preferences.
- Diabetes Educator: If you have prediabetes or diabetes, a diabetes educator can teach you practical skills for managing your condition.
Build a Support System
You don't have to do this alone!
- Family and Friends: Share your goals with loved ones and ask for their support. They can help you stay motivated and make healthy choices together.
- Support Groups: Connecting with others who are also managing their blood sugar can provide encouragement, tips, and a sense of community.
- Online Communities: Many online forums and groups offer a platform to share experiences and get advice.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Even with the best intentions, it's easy to fall into common traps that can make it harder to maintain a normal blood sugar reading. Being aware of these can help you steer clear!
- Ignoring Blood Sugar Spikes: It's tempting to brush off a high reading, especially if you feel fine. However, consistent spikes, even if not extremely high, can cause damage over time. Pay attention to what causes them.
- Skipping Meals: This can lead to very low blood sugar, which then often results in overeating or making poor food choices at the next meal, causing a big spike.
- Too Many Sugary Drinks: Sodas, fruit juices (even 100% juice), and sweetened coffees are liquid sugar that hits your bloodstream fast, causing rapid and significant blood sugar increases.
- Not Reading Food Labels: Many processed foods hide sugars and unhealthy carbs. Always check nutrition labels for sugar content, fiber, and serving sizes.
- Lack of Consistency: Sporadic healthy habits won't lead to stable blood sugar. It's the daily, consistent effort that makes the biggest difference.
- Over-relying on “Diabetic” or “Diet” Foods: These can still contain hidden carbs or artificial sweeteners that might impact your blood sugar or gut health. Focus on whole, unprocessed foods instead.
- Ignoring Stress and Sleep: As discussed, these factors are powerful blood sugar disruptors. Don't underestimate their impact.
- Not Consulting Your Doctor: Self-managing without professional guidance can be risky. Your doctor is your best resource for personalized advice and medical adjustments.
By avoiding these common pitfalls and focusing on the positive strategies outlined, you'll be well on your way to enjoying stable blood sugar and better health and beyond!
Conclusion
Achieving and maintaining a normal blood sugar reading daily is a powerful step towards a healthier, more energetic life. It's a journey that combines mindful eating, regular physical activity, effective stress management, quality sleep, and consistent monitoring. Remember, every small, positive choice you make adds up to significant improvements in your overall well-being.
By understanding how your body works, making informed lifestyle choices, and working closely with your healthcare team, you can take control of your blood sugar. Empower yourself with knowledge, embrace healthy habits, and enjoy the benefits of stable blood sugar: more energy, better mood, and a reduced risk of long-term health complications. Start today – your body will thank you!








