Understanding your health has never been more important. Among the many health topics we discuss, diabetes mellitus often comes up. But what exactly is it? For many, the term sounds complicated, full of medical jargon and scary implications. The truth is, understanding diabetes doesn't have to be hard.

This guide will break down diabetes mellitus into simple, easy-to-understand terms, helping you grasp the basics, recognize the signs, and learn how to manage or even prevent it. Whether you're curious for yourself, a loved one, or just want to be more informed, you're in the right place. Let’s demystify diabetes together.
Key Takeaways
- Diabetes Mellitus is About Blood Sugar: It's a health condition where your body has trouble managing its blood sugar (glucose) levels, leading to them being too high.
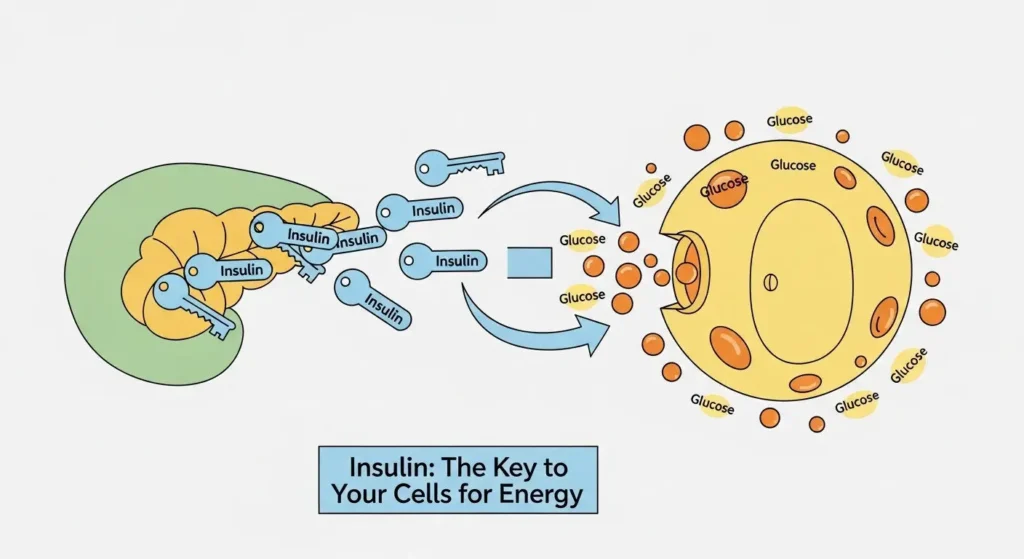
- Insulin is Key: A hormone called insulin, made by your pancreas, acts like a key to let sugar into your cells for energy. In diabetes, this key either doesn't work well or isn't made enough.
- Two Main Types: Type 1 diabetes is when your body doesn't make insulin. Type 2 diabetes, which is more common, is when your body doesn't use insulin well or doesn't make enough.
- Lifestyle Matters: Healthy eating, regular exercise, and maintaining a healthy weight are crucial for preventing and managing Type 2 diabetes.
- Early Detection is Vital: Knowing the signs and getting regular check-ups can help catch diabetes early, preventing serious health problems down the road.
What is Diabetes Mellitus? The Basics
Imagine your body as a car that needs fuel to run. That fuel is sugar, specifically glucose, which comes from the food you eat. After you eat, your digestive system breaks down food into glucose, which then enters your bloodstream.
Now, for your body's cells to use this glucose for energy, they need a special “key” to unlock their doors. This key is a hormone called insulin. Insulin is made by an organ behind your stomach called the pancreas.
Here’s how it should work:
- You eat food.
- Food turns into glucose (sugar) in your blood.
- Your pancreas releases insulin.
- Insulin acts like a key, opening your cells so glucose can get in and be used for energy.
- Your blood sugar levels stay balanced.
With diabetes mellitus, this system goes wrong. Either your pancreas doesn't make enough insulin, or your body's cells don't respond well to the insulin that is made. This means glucose can't get into your cells effectively, so it builds up in your bloodstream. High blood sugar over time can lead to serious health problems.
Think of it this way:
- Not enough keys (insulin): The doors stay locked, and sugar piles up outside.
- Keys don't fit the locks (insulin resistance): The doors stay locked, and sugar piles up outside.
Types of Diabetes Mellitus
Diabetes isn't a single condition; it comes in different forms. The two most common are Type 1 and Type 2, but there are others too. Understanding the differences is important.
Type 1 Diabetes: The “No Keys” Problem
Type 1 diabetes is less common, affecting about 5-10% of people with diabetes. It's an autoimmune disease. This means your body's immune system, which usually fights off germs, mistakenly attacks and destroys the cells in your pancreas that make insulin.
- What happens: Your body stops making insulin completely, or makes very little.
- Who gets it: It often develops in children, teens, or young adults, but can appear at any age. It's not caused by diet or lifestyle.
- Treatment: People with Type 1 diabetes must take insulin every day to live. There's no cure, but it can be managed.
Type 2 Diabetes: The “Keys Don't Fit” Problem
Type 2 diabetes is the most common form, accounting for 90-95% of all diabetes cases. In Type 2 diabetes, your body either doesn't use insulin well (this is called insulin resistance) or it doesn't make enough insulin to keep blood sugar levels normal.
- What happens: At first, your pancreas tries to make more insulin to compensate. But over time, it can't keep up, and blood sugar levels rise.
- Who gets it: It usually develops in adults, though it's increasingly seen in children and teens. Lifestyle factors like being overweight, inactive, and having a family history play a big role.
- Treatment: It can often be managed with healthy eating, regular exercise, and sometimes oral medications or insulin. It can sometimes be prevented or even reversed, especially if caught early.
Prediabetes: The Warning Sign
Prediabetes means your blood sugar levels are higher than normal, but not yet high enough to be diagnosed as Type 2 diabetes. It's a critical warning sign!
- What happens: Your body is starting to have trouble with insulin, but it's not too late to make changes.
- Why it matters: Without lifestyle changes, prediabetes often leads to Type 2 diabetes within 5-10 years.
- The good news: This is your chance to turn things around! Healthy eating and increased physical activity can bring blood sugar levels back to normal.
Gestational Diabetes: Diabetes During Pregnancy
Some women develop diabetes during pregnancy. This is called gestational diabetes.
- What happens: Hormones from pregnancy can make cells less sensitive to insulin.
- Why it matters: It can cause health problems for both the mother and the baby if not managed.
- Treatment: Often managed with diet and exercise, but sometimes insulin is needed. It usually goes away after the baby is born, but it does increase the mother's risk of developing Type 2 diabetes later in life.
How Diabetes Mellitus Affects Your Body
When blood sugar levels stay high for a long time, it can damage many parts of your body. Think of it like a constant, silent stress on your system.
Here are some of the ways diabetes mellitus can affect your body:
- Heart and Blood Vessels: High blood sugar can damage blood vessels, increasing the risk of heart disease, heart attacks, and strokes.
- Kidneys: Your kidneys work hard to filter your blood. High blood sugar can damage these filters, potentially leading to kidney disease or even kidney failure.
- Eyes: Diabetes can harm the tiny blood vessels in your eyes, leading to vision problems, including blindness, if not treated. This is called diabetic retinopathy.
- Nerves: High blood sugar can damage nerves throughout your body, especially in your legs and feet. This can cause numbness, tingling, pain, or weakness. This is known as diabetic neuropathy.
- Feet: Nerve damage and poor circulation from diabetes mellitus can make foot injuries harder to heal and increase the risk of infections. Serious cases can even lead to amputations.
- Skin: People with diabetes are more prone to skin infections and other skin conditions.
- Dental Health: Diabetes can make you more susceptible to gum disease and other dental problems.
Pull Quote: “Diabetes mellitus is a marathon, not a sprint. Consistent effort in managing your blood sugar can prevent serious complications and help you live a full, healthy life.”
Signs and Symptoms: What to Look For
The tricky thing about diabetes mellitus, especially Type 2, is that it can develop slowly, and symptoms might be mild at first, making them easy to miss. However, recognizing these signs can lead to earlier diagnosis and better management.
Common signs and symptoms of diabetes mellitus include:
- Increased Thirst (Polydipsia): Feeling thirsty all the time, no matter how much you drink.
- Frequent Urination (Polyuria): Having to go to the bathroom a lot, especially at night.
- Increased Hunger (Polyphagia): Feeling very hungry, even after eating.
- Unexplained Weight Loss: Losing weight without trying, especially in Type 1 diabetes.
- Fatigue: Feeling tired and lacking energy, even if you're getting enough sleep.
- Blurred Vision: High blood sugar can pull fluid from the lenses of your eyes.
- Slow-Healing Sores or Frequent Infections: Cuts and bruises might take longer to heal, and you might get more infections (skin, gums, bladder).
- Tingling or Numbness: In your hands or feet (a sign of nerve damage).
If you notice any of these symptoms, it’s important to talk to your doctor.
Diagnosing Diabetes Mellitus: Getting Checked
Diagnosing diabetes mellitus usually involves simple blood tests. Your doctor will likely check your blood sugar levels using one or more of these tests:
- Fasting Plasma Glucose (FPG) Test: Measures your blood sugar after an overnight fast (no food or drink for at least 8 hours).
- Normal: Less than 100 mg/dL
- Prediabetes: 100 to 125 mg/dL
- Diabetes: 126 mg/dL or higher
- A1C Test (Glycated Hemoglobin Test): This test gives you an average of your blood sugar levels over the past 2-3 months. It doesn't require fasting.
- Normal: Below 5.7%
- Prediabetes: 5.7% to 6.4%
- Diabetes: 6.5% or higher
- Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT): Measures your blood sugar before and 2 hours after you drink a special sweet liquid.
- Normal: Less than 140 mg/dL at 2 hours
- Prediabetes: 140 to 199 mg/dL at 2 hours
- Diabetes: 200 mg/dL or higher at 2 hours
- Random Plasma Glucose Test: This test can be done at any time, regardless of when you last ate. If your blood sugar is 200 mg/dL or higher, along with symptoms of diabetes, it suggests diabetes.
Getting tested is easy and quick. If you have risk factors for diabetes (like being overweight, having a family history, or being over 45), talk to your doctor about getting screened regularly in 2025.
Managing Diabetes: Taking Control
Managing diabetes is about keeping your blood sugar levels as close to normal as possible to prevent complications. It's a team effort between you and your healthcare providers.
1. Diet and Nutrition: Fueling Your Body Wisely
What you eat has a huge impact on your blood sugar. It's not about “eating no sugar” but about making smart choices.
- Focus on Whole Foods: Load up on vegetables, fruits, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
- Watch Your Carbs: Carbohydrates turn into glucose. Learn about carb counting and how different carbs affect your blood sugar. Your doctor or a dietitian can help.
- Portion Control: Eating appropriate serving sizes is key.
- Limit Processed Foods: Sugary drinks, fast food, and highly processed snacks can spike blood sugar.
2. Exercise and Physical Activity: Get Moving!
Regular physical activity is incredibly beneficial for everyone, but especially for people with diabetes or prediabetes. Exercise helps your body use insulin more effectively and can even help cells take in glucose without insulin.
- Aim for Consistency: Try for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week.
- Mix It Up: Combine aerobic activities (like brisk walking, swimming, cycling) with strength training (like lifting weights or body weight loss exercise).
- Benefits: Exercise can help you lose weight, lower blood pressure, improve cholesterol levels, and reduce stress. If you're looking for the best exercise to lose weight or specifically the best exercise to lose belly fat, incorporating a variety of movements is often most effective. Always check with your doctor before starting a new exercise program.
3. Medication: When Lifestyle Isn't Enough
For many with Type 2 diabetes, lifestyle changes are a powerful first step. However, some people will also need medication.
- Oral Medications: These pills can work in different ways, such as helping your body make more insulin, helping your body use insulin better, or slowing down sugar absorption.
- Insulin: People with Type 1 diabetes must take insulin. Some people with Type 2 diabetes also need insulin if their pancreas can no longer produce enough on its own. Insulin is given by injection or through an insulin pump.
4. Monitoring Blood Sugar: Stay Informed
Regularly checking your blood sugar levels helps you and your doctor understand how food, exercise, stress, and medication affect you.
- Home Monitoring: You'll use a blood glucose meter to check your levels throughout the day.
- Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGMs): These devices wear on your skin and provide real-time blood sugar readings, which can be very helpful for some people.
5. Other Lifestyle Changes: Holistic Health
- Stress Management: Stress can raise blood sugar levels. Find healthy ways to cope, like meditation, yoga, or hobbies.
- Quality Sleep: Poor sleep can affect insulin sensitivity. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night.
- Quit Smoking: Smoking significantly increases the risk of diabetes mellitus complications.
- Limit Alcohol: Alcohol can affect blood sugar levels, sometimes causing them to drop too low.
- Consider Green Tea: Some studies suggest that how green tea help lose weight and its potential benefits for blood sugar regulation might be a supportive addition to a healthy lifestyle.
Preventing Type 2 Diabetes and Prediabetes
The great news about Type 2 diabetes and prediabetes is that they are often preventable! Even small changes can make a big difference.
Here’s your prevention playbook for 2025:
- Eat Healthily: Choose whole, unprocessed foods. Limit sugary drinks, refined grains, and unhealthy fats.
- Stay Active: Get at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise each week. Find activities you enjoy!
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Losing even a small amount of weight (5-7% of your body weight) if you are overweight can significantly reduce your risk.
- Don't Smoke: If you smoke, quitting is one of the best things you can do for your overall health and to reduce your diabetes risk.
- Regular Check-ups: Talk to your doctor about your risk factors and get screened regularly.
Living Well with Diabetes
Living with diabetes mellitus doesn't mean your life has to stop. With the right knowledge, tools, and support, you can lead a full and active life. In 2025, there are more resources than ever before:
- Advanced Technology: From smart insulin pens to continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) that connect to your phone, technology is making management easier and more precise.
- Support Networks: Online communities, local support groups, and diabetes educators offer invaluable guidance and encouragement.
- Personalized Care: Healthcare providers are increasingly focused on tailoring treatment plans to individual needs and lifestyles.
- Research Breakthroughs: Ongoing research continues to improve treatments and offers hope for new prevention strategies and even cures.

The Role of Supplements: A Closer Look
Many people with diabetes or those at risk consider supplements. While some supplements might support overall health, it's crucial to approach them with caution and always discuss them with your doctor. No supplement can cure diabetes or replace prescribed medications and lifestyle changes.
For example, some people explore supplements like Mitolyn, which focuses on mitochondrial health. While exciting research is ongoing in areas like cellular energy and metabolism, it's important to remember that such products are typically designed to support general well-being, not to treat specific medical conditions like diabetes. If you're considering a supplement like those discussed in a Mitolyn review, ensure you understand its purpose and potential interactions with any medications you might be taking. Always prioritize evidence-based treatments and discuss all health decisions with your healthcare team.
Important Note: Always consult your doctor or a registered dietitian before starting any new supplement regimen, especially if you have diabetes or other health conditions.
Common Myths About Diabetes
Let's clear up some common misunderstandings about diabetes:
- Myth: Only overweight people get Type 2 diabetes.
- Fact: While being overweight is a major risk factor, people of all shapes and sizes can get Type 2 diabetes. Other factors like genetics, age, and ethnicity play a role.
- Myth: Eating too much sugar causes diabetes.
- Fact: Eating too much sugar doesn't directly cause Type 1 diabetes. For Type 2, while a diet high in sugar can contribute to weight gain and insulin resistance, it's not the sole cause. It's a complex interaction of genetics and lifestyle.
- Myth: People with diabetes can't eat any sugar or carbs.
- Fact: People with diabetes can eat sugar and carbs in moderation as part of a balanced meal plan. The key is portion control and choosing healthier sources of carbohydrates like whole grains, fruits, and vegetables.
- Myth: Diabetes isn't a serious disease.
- Fact: Diabetes is a serious chronic condition that, if not managed, can lead to severe complications like heart disease, kidney failure, blindness, and amputations.
- Myth: Insulin is a sign of failure.
- Fact: Taking insulin is a necessary and effective treatment for many people with diabetes. It's a tool to keep you healthy, not a sign that you've failed to manage your condition.
When to See a Doctor
If you suspect you might have diabetes, or if you have any of the symptoms mentioned, don't delay – see your doctor right away. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for preventing long-term complications.
Even if you don't have symptoms, consider regular check-ups if you:
- Are overweight or obese.
- Are 45 years or older.
- Have a family history of diabetes.
- Have had gestational diabetes.
- Have high blood pressure or high cholesterol.
- Are physically inactive.
Your doctor can assess your risk and recommend appropriate screening tests for diabetes mellitus.
Conclusion
Understanding diabetes mellitus in simple terms is the first step toward taking control of your health. It's a condition where your body struggles to manage blood sugar, primarily due to issues with insulin. While Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune condition requiring insulin, Type 2 diabetes is often linked to lifestyle and can frequently be prevented or managed through healthy choices.
Remember, you are not alone in this journey. With the right information, a proactive approach to diet and exercise, and the support of your healthcare team, you can effectively manage diabetes or significantly reduce your risk of developing it. Make 2025 the year you prioritize your well-being and empower yourself with knowledge!








