Introduction: What is Diabetes?
Diabetes is a chronic metabolic disorder characterized by elevated blood glucose (sugar) levels due to the body’s inability to produce or effectively use insulin . Insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas, acts as a “key” that allows glucose to enter cells for energy production . When this process is disrupted, hyperglycemia (high blood sugar) occurs, leading to long-term health complications .

Globally, over 537 million adults live with diabetes, a number projected to rise to 783 million by 2045 . This guide explores the types, causes, symptoms, and management strategies for diabetes, empowering readers to take control of their health.
Types of Diabetes: Understanding the Differences

1. Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes (T1D) is an autoimmune condition where the body’s immune system attacks insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas . This results in little or no insulin production, requiring lifelong insulin therapy . T1D typically develops in children or young adults but can occur at any age .
2. Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes (T2D) accounts for 90–95% of cases and occurs when the body becomes resistant to insulin or the pancreas fails to produce enough insulin . Risk factors include obesity, sedentary lifestyle, and genetics . T2D was historically diagnosed in adults but is now increasingly common in adolescents .
3. Gestational Diabetes
This form develops during pregnancy due to hormonal changes that impair insulin function . While it often resolves postpartum, it increases the risk of developing T2D later in life .
4. Other Types
Rare forms include monogenic diabetes (genetic mutations) and secondary diabetes caused by conditions like cystic fibrosis or medications (e.g., corticosteroids) .
Causes and Risk Factors: Why Does Diabetes Develop?
Core Mechanisms
Diabetes arises from insulin deficiency or resistance . In T1D, immune-mediated beta-cell destruction halts insulin production . In T2D, excess weight and inactivity reduce insulin sensitivity, overburdening the pancreas .
Key Risk Factors
- Genetics : Family history of diabetes increases risk .
- Lifestyle : Poor diet, physical inactivity, and obesity are major contributors to T2D .
- Age : Risk of T2D rises after age 45 .
- Ethnicity : Higher prevalence in Black, Hispanic, and Asian populations .
Symptoms of Diabetes: Recognizing the Warning Signs
Common symptoms include:
- Frequent urination and excessive thirst
- Unexplained weight loss (T1D) or slow-healing wounds (T2D)
- Fatigue and blurred vision due to high blood sugar levels
T2D symptoms often develop gradually, leading to delayed diagnosis .

Diagnosis: How Is Diabetes Identified?
Key Diagnostic Tests
- Fasting Blood Glucose Test :
- Normal: <100 mg/dL
- Prediabetes: 100–125 mg/dL
- Diabetes: ≥126 mg/dL
- HbA1c Test :
- Normal: <5.7%
- Prediabetes: 5.7–6.4%
- Diabetes: ≥6.5%
- Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT) :
Used primarily for gestational diabetes .
Early detection through these tests is critical to prevent complications .
Managing Diabetes: Treatment and Lifestyle Strategies
1. Type 1 Diabetes Management
- Insulin therapy (injections or pumps)
- Blood sugar monitoring via continuous glucose monitors (CGMs)
2. Type 2 Diabetes Management
- Lifestyle changes : Weight loss, balanced diet, and 150 minutes of weekly exercise
- Medications : Metformin, GLP-1 receptor agonists, or insulin if needed
3. Gestational Diabetes Management
- Dietary adjustments and regular blood sugar checks

Prevention: Can Diabetes Be Avoided?
For Type 1 Diabetes
Currently, no known prevention methods exist, though research into immunotherapies is ongoing .
For Type 2 Diabetes
- Weight loss : Losing 5–10% of body weight reduces risk by 58%
- Physical activity : Brisk walking for 30 minutes daily lowers risk
- Diet : Prioritize fiber-rich foods and limit processed sugars
Prediabetes is reversible with these interventions .
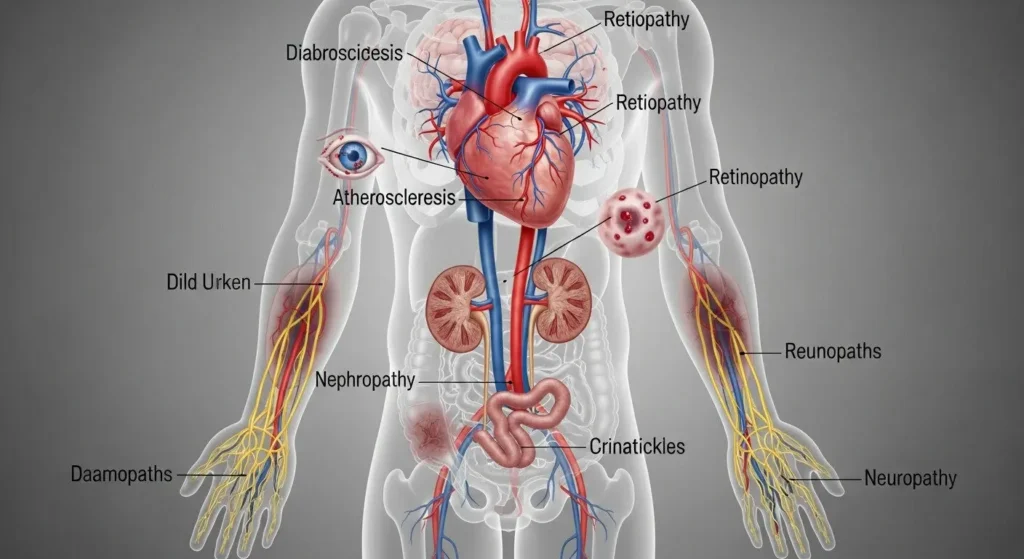
Complications of Diabetes: What Happens If It’s Untreated?
Chronic hyperglycemia damages organs and systems, leading to:
- Cardiovascular disease (heart attacks, strokes)
- Neuropathy (nerve damage) and retinopathy (vision loss)
- Kidney failure requiring dialysis
Proactive management (A1c <7%) significantly reduces complication risks .
The Latest Research and Innovations in Diabetes Care
Advances in Treatment
- Bionic pancreas : Automated insulin delivery systems
- GLP-1 drugs (e.g., semaglutide) for weight loss and blood sugar control
- Artificial intelligence in glucose monitoring
Promising Research
- Beta-cell regeneration therapies for T1D
- Gene editing to correct monogenic diabetes
Expert Resources and Support for People with Diabetes
Trusted Organizations
- World Health Organization (WHO) – Global diabetes guidelines .
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) – Prevention programs .
- American Diabetes Association (ADA) – Advocacy and education .
Conclusion: Taking Control of Diabetes
Diabetes is a manageable condition with early diagnosis, lifestyle changes, and medical care. By understanding the risks, symptoms, and treatment options, individuals can prevent complications and lead fulfilling lives.








