Sun-kissed skin might look good for a moment, but the long-term cost can be severe. Skin cancer is the most common type of cancer, affecting millions worldwide. The good news? It's also one of the most preventable. Taking proactive steps to protect your skin is more important than ever. This guide will give you all the essential skin cancer prevention strategies you need to stay safe, healthy, and informed.

Key Takeaways
- Sun Protection is Your Shield: Always protect your skin from the sun's powerful UV rays using sunscreen, hats, sunglasses, and protective clothing.
- Seek Shade, Especially Midday: Limit your direct sun exposure during peak hours (10 AM to 4 PM) when UV radiation is strongest.
- Say NO to Tanning Beds: Tanning beds are not a safe alternative to sun exposure and significantly increase your risk of skin cancer.
- Know Your Skin: Perform Regular Checks: Learn the ABCDEs of melanoma and check your skin monthly for any new or changing spots.
- Get Professional Help: Schedule annual skin exams with a dermatologist, especially if you have risk factors or notice anything suspicious.
Understanding Skin Cancer Prevention: Why Prevention Matters
Skin cancer starts when skin cells grow out of control, usually due to damage from the sun's ultraviolet (UV) rays. It's a serious condition, but when caught early, it's often treatable. Knowing the basics helps you understand why prevention is so crucial.
There are three main types of skin cancer:
- Basal Cell Carcinoma (BCC): This is the most common type, making up about 80% of all skin cancers. It often appears as a pearly or waxy bump, a flat, flesh-colored or brown lesion, or a bleeding sore that won't heal. BCCs usually grow slowly and rarely spread to other parts of the body, but awareness plays a key role in Skin Cancer Prevention.
- Squamous Cell Carcinoma (SCC): The second most common type, SCCs often look like firm, red nodules, or flat, scaly, crusty lesions. They can develop on sun-exposed areas like the face, ears, neck, and hands. SCCs can grow and spread if not treated, though this is less common than with melanoma.
- Melanoma: This is the most dangerous type of skin cancer. While less common, it's more likely to grow and spread to other parts of the body if not caught early. Melanoma often develops from existing moles or appears as a new dark spot.
The Silent Threat: UV Radiation
The sun gives off two main types of ultraviolet (UV) rays that reach the Earth's surface and can harm your skin:
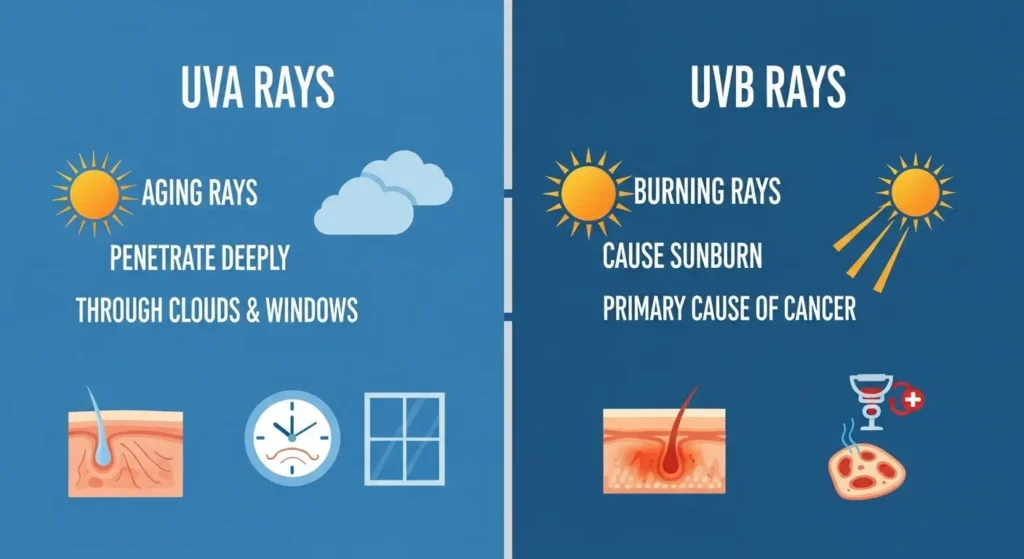
- UVA Rays: These rays contribute to skin aging (wrinkles, age spots) and can also cause skin cancer. They can pass through windows and clouds.
- UVB Rays: These are the primary cause of sunburn and play a key role in developing most skin cancers. Their intensity varies by season, time of day, and location.
Both UVA and UVB rays damage the DNA in your skin cells, leading to mutations that can cause cancer. There's no such thing as a “safe tan” – a tan is a sign of skin damage.
Your First Line of Defense: Sunscreen Savvy
Sunscreen is a powerful tool in your skin cancer prevention arsenal. But it only works if you use it correctly!
Choosing the Right Sunscreen
When you're browsing the shelves, look for these key features:
- Broad-Spectrum: This means the sunscreen protects against both UVA and UVB rays. It's non-negotiable!
- SPF 30 or Higher: SPF stands for Sun Protection Factor. An SPF 30 blocks about 97% of UVB rays, while SPF 50 blocks about 98%. Higher SPFs offer only slightly more protection.
- Water-Resistant: If you're swimming or sweating, this is crucial. Water-resistant sunscreens protect for 40 or 80 minutes, but they are not waterproof and still need reapplication.
“Think of sunscreen as your daily armor against invisible threats. It's not just for beach days; it's for every day the sun shines.”
How to Apply Sunscreen Like a Pro
- Use Enough: Most adults need about one ounce (a shot glass full) to cover their entire body. Don't skimp!
- Apply Early: Put sunscreen on 15-30 minutes before going outside. This gives your skin time to absorb it and form a protective barrier.
- Cover All Exposed Skin: Don't forget often-missed spots like your ears, neck, tops of your feet, scalp (if bald or thin hair), and lips (use an SPF lip balm).
- Reapply Often: This is where many people fall short. Reapply at least every two hours, or more often if you're swimming, sweating heavily, or towel drying. Even “all-day” formulas lose effectiveness.
| Sunscreen Type | Best For | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mineral (Zinc Oxide, Titanium Dioxide) | Sensitive skin, children, daily use | Physical barrier, works immediately, less irritating | Can leave a white cast, thicker texture |
| Chemical (Oxybenzone, Avobenzone, etc.) | Active individuals, sheer finish | Lighter feel, no white cast, easier to rub in | Needs 15-30 min to activate, can irritate sensitive skin |
| Stick | Face, ears, touch-ups | Easy to apply, portable, good for specific areas | Can be hard to get full coverage |
| Spray | Body, hard-to-reach areas | Quick application, convenient | Risk of uneven coverage, inhalation concerns |

Pro Tip: Check the expiration date! Sunscreen loses its effectiveness over time. Most sunscreens are good for about three years.
Beyond the Bottle: Protective Clothing and Shade
While sunscreen is vital, it's not your only defense. Combining it with other protective measures gives you the best chance against sun damage.
Dress for Success: Your UV-Blocking Wardrobe
Think of your clothes as a physical barrier against UV rays.
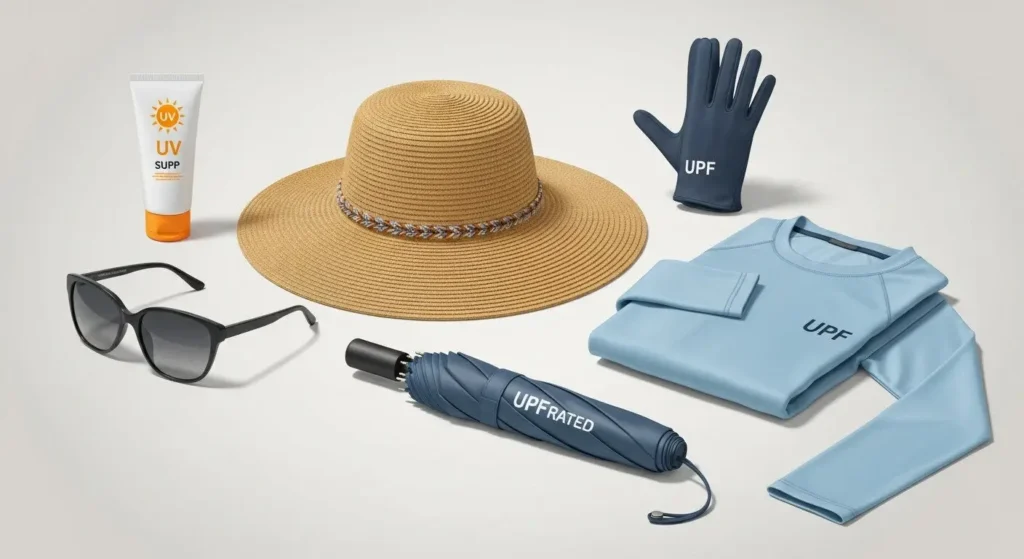
- Wide-Brimmed Hats: A hat with a brim at least 3 inches wide all around protects your scalp, ears, face, and neck. Baseball caps are better than nothing, but they don't protect your ears or neck.
- UV-Blocking Sunglasses: Look for sunglasses that block 99% or 100% of UVA and UVB rays. This protects your eyes from cataracts and the delicate skin around them from cancer.
- Long Sleeves and Pants: Lightweight, loose-fitting clothing made from tightly woven fabrics offers excellent protection. Some clothing even comes with an Ultraviolet Protection Factor (UPF) rating – the higher the UPF, the better the protection. A UPF of 30+ is recommended.
- Darker Colors: Darker or brighter colors tend to absorb more UV rays than lighter colors, which means fewer rays reach your skin.

The Power of Shade
Seeking shade is one of the easiest and most effective ways to reduce your sun exposure.
- Peak Hours: The sun's UV rays are strongest between 10 AM and 4 PM. If possible, plan your outdoor activities before or after these hours.
- Natural Shade: Trees, umbrellas, and awnings offer great protection.
- Artificial Shade: If natural shade isn't available, bring your own! A beach umbrella or pop-up tent can be a lifesaver.
- Cloudy Days Aren't Safe Days: UV rays can penetrate clouds. Don't let a cloudy sky fool you into thinking you're safe from the sun.
Remember, a combination of these methods is always best. Sunscreen + hat + sunglasses + shade = maximum protection!
The Dark Side of Tanning: Why Tanning Beds are a Big NO
Despite what some myths suggest, there's no such thing as a “safe tan,” especially not from a tanning bed. Tanning beds emit UV radiation that is often many times stronger than the midday sun.
The Dangers Are Real:
- Increased Skin Cancer Risk: Using tanning beds significantly increases your risk of developing all types of skin cancer, including melanoma. Studies show that just one indoor tanning session can increase your risk of melanoma by 20%, basal cell carcinoma by 29%, and squamous cell carcinoma by 67%, making avoidance an important step in Skin Cancer Prevention.
- Premature Aging: Tanning bed use accelerates skin aging, leading to wrinkles, fine lines, and age spots much earlier in life.
- Eye Damage: Without proper eye protection, UV radiation from tanning beds can damage your eyes, increasing the risk of cataracts and other eye problems.
- Weakened Immune System: Excessive UV exposure can suppress your immune system, making you more vulnerable to infections and diseases.
A Word of Caution: Some people believe a “base tan” protects them from sunburn. This is a dangerous myth. A base tan is still skin damage, and it offers minimal protection – equivalent to an SPF of about 3 or less. It's not worth the risk.
For a healthy glow, consider sunless tanning lotions or sprays. They give you a tanned look without the harmful UV exposure.
Your Skin's Early Warning System: Self-Checks and Professional Help
Even with the best prevention efforts, it's crucial to be vigilant about changes in your skin. Early detection of skin cancer dramatically improves treatment outcomes and plays a vital role in Skin Cancer Prevention.
The ABCDEs of Melanoma: What to Look For
Learning the “ABCDEs” is a simple but powerful way to monitor your moles and spots for potential signs of melanoma. Look for these changes when you examine your skin:
| Letter | What it Stands For | What to Look For |
|---|---|---|
| A | Asymmetry | One half of the mole does not match the other half. |
| B | Border | The edges are irregular, ragged, notched, or blurred. |
| C | Color | The color is not the same all over and may include shades of brown or black, sometimes with patches of pink, red, white, or blue. |
| D | Diameter | The spot is larger than 6 millimeters (about the size of a pencil eraser), though melanomas can sometimes be smaller. |
| E | Evolving | The mole is changing in size, shape, color, or elevation, or any new symptom appears, such as bleeding, itching, or crusting. |
How to Perform a Monthly Self-Skin Exam
Make it a habit to check your skin from head to toe once a month.
- Get Ready: Find a well-lit room, use a full-length mirror, and have a hand mirror handy for hard-to-see areas.
- Face and Neck: Examine your face, nose, lips, mouth, and ears. Don't forget your scalp (use a comb or blow dryer to part your hair).
- Hands and Arms: Check the front and back of your hands, between your fingers, and under your fingernails. Move up your arms to your elbows, including underarms.
- Torso: Examine your chest, abdomen, and back (use the hand mirror for your back).
- Legs and Feet: Check the front and back of your legs, including your groin area. Don't forget the tops of your feet, between your toes, and the soles of your feet.
- Buttocks: Use the hand mirror to check this area.
If you notice any new moles, spots, or changes to existing ones that fit the ABCDE criteria, or any other suspicious lesions, contact a dermatologist right away. Early detection is key!
The Importance of Professional Skin Exams
While self-checks are important, they don't replace a professional eye. A dermatologist is trained to spot suspicious lesions that you might miss.
- When to Go: Most people should have a full-body skin exam annually. If you have a high risk (e.g., many moles, family history of melanoma, fair skin, history of severe sunburns), your dermatologist might recommend more frequent checks.
- What to Expect: During the exam, the dermatologist will carefully check your entire skin surface, often using a magnifying tool called a dermatoscope. It's usually quick and painless.
Remember: Don't hesitate to point out any spots that concern you, even if the doctor doesn't immediately focus on them. You know your skin best!
Beyond the Sun: Holistic Skin Health and Prevention
While sun protection is the cornerstone of skin cancer prevention, your overall lifestyle and health choices also play a significant role in maintaining healthy skin and a strong immune system.

The Power of Nutrition
What you eat can affect your skin's health and its ability to repair itself.
- Antioxidant-Rich Foods: Foods packed with antioxidants can help protect your cells from damage, including damage caused by UV radiation. Think colorful fruits and vegetables like berries, leafy greens (spinach, kale), tomatoes, carrots, and bell peppers.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Found in fatty fish (salmon, mackerel), flaxseeds, and walnuts, omega-3s can help reduce inflammation and support overall skin health.
- Vitamin D: While sun exposure is a primary source of Vitamin D, it's best to get it safely through diet (fatty fish, fortified foods) or supplements to avoid UV damage. Discuss this with your doctor.
“Nourish your body from the inside out. A healthy diet not only benefits your skin but your entire well-being, paving the way for a healthier YOU.”
Stay Hydrated
Drinking enough water is essential for healthy skin. Hydrated skin is more resilient and can better perform its protective functions. Aim for at least 8 glasses of water a day.
Lifestyle Choices Matter
- Avoid Smoking: Smoking significantly damages skin cells and blood vessels, leading to premature aging and increasing the risk of various cancers, including squamous cell carcinoma. Quitting smoking is one of the best things you can do for your overall health.
- Limit Alcohol: Excessive alcohol consumption can dehydrate your skin and contribute to inflammation, potentially affecting skin health.
Just as we prioritize skin health and focus on Skin Cancer Prevention, other aspects of our well-being are also crucial for a full and vibrant life. For instance, maintaining a healthy weight is another pillar of overall wellness, and some people explore options to support their goals. Similarly, as men age, understanding men's health concerns such as prostate health becomes increasingly important. Taking proactive steps for prostate health can involve various approaches, and some individuals may look into seeking effective prostate supplements or learning about tackling prostate problems as part of their comprehensive health management strategy. These holistic approaches underscore the importance of caring for your entire body, not just isolated parts.
Special Considerations and Debunking Myths
Skin cancer prevention isn't one-size-fits-all. Some groups need extra vigilance, and some common beliefs about sun exposure are simply wrong.
Who Needs Extra Care?
- Children and Babies: Their skin is much more delicate and susceptible to sun damage. Sunburns in childhood significantly increase the risk of melanoma later in life.
- Keep babies under 6 months out of direct sun.
- Use broad-spectrum sunscreen (SPF 30+) on children over 6 months, along with protective clothing and shade.
- Teach sun safety habits early!
- People with Fair Skin, Red Hair, or Light Eyes: These individuals have less melanin (the pigment that gives skin color and offers some natural protection) and are at a higher risk of sun damage and skin cancer, highlighting the importance of Skin Cancer Prevention.
- Those with Many Moles or Atypical Moles: More moles, especially large or unusually shaped ones, increase your risk. Regular self-checks and professional exams are vital.
- Individuals with a Family History of Skin Cancer: Genetics play a role. If a close family member has had melanoma, your risk is higher.
- Outdoor Workers and Athletes: People who spend a lot of time outdoors for work or recreation have increased cumulative sun exposure, making consistent sun protection essential.
- People Living at High Altitudes or Near the Equator: UV radiation is stronger in these areas.
Debunking Common Sun Myths
Let's clear up some dangerous misconceptions:
- Myth 1: “A base tan protects you from sunburn.”
- Fact: A tan is skin damage. A base tan offers minimal SPF (around 3) and does not protect against further damage or skin cancer, underscoring the importance of Skin Cancer Prevention.
- Myth 2: “You only need sunscreen on sunny days.”
- Fact: Up to 80% of the sun's UV rays can penetrate clouds. You need sun protection every day, regardless of the weather.
- Myth 3: “People with dark skin don't get skin cancer.”
- Fact: While melanin offers some natural protection, people of all skin tones can get skin cancer. It's often diagnosed later in individuals with darker skin, making it more dangerous and reinforcing the need for Skin Cancer Prevention.
- Myth 4: “I don't need sunscreen if I'm only outside for a few minutes.”
- Fact: Cumulative sun exposure adds up over time. Even short, unprotected exposures contribute to skin damage and increase risk. Make sunscreen a daily habit.
- Myth 5: “Sunscreen blocks Vitamin D absorption, so I need sun exposure.”
- Fact: While sunscreen does block some UV, most people still get enough Vitamin D through incidental sun exposure, diet, or supplements. The health risks of unprotected sun exposure far outweigh the benefits of producing Vitamin D this way.
Knowing the facts empowers you to make smarter choices for your skin's health.
Your Skin Protection Action Plan: Simple Steps for a Safer Year! ✅
Making skin cancer prevention a priority doesn't have to be complicated. By adopting a few consistent habits, you can significantly reduce your risk and protect your skin for years to come.
Here's your actionable plan:
- Embrace Daily Sunscreen: Make broad-spectrum SPF 30+ sunscreen a non-negotiable part of your morning routine, just like brushing your teeth. Reapply religiously when outdoors.
- Gear Up for the Outdoors: Always grab a wide-brimmed hat, UV-blocking sunglasses, and consider UPF protective clothing before stepping out.
- Befriend the Shade: Plan outdoor activities for early morning or late afternoon, and always look for natural or artificial shade during peak sun hours (10 AM – 4 PM).
- Cut Out Tanning Beds: If you've ever used them, commit to never using them again. Explore sunless tanning options if you desire a bronzed look.
- Become a Skin Detective: Dedicate a few minutes each month to perform a thorough self-skin exam, using the ABCDE rule to spot any suspicious changes.
- Partner with a Pro: Schedule your annual professional skin exam with a dermatologist. This is especially vital if you have any risk factors or concerns.
- Nourish Your Skin from Within: Support your skin's health with a diet rich in antioxidants and stay well-hydrated.
- Educate and Advocate: Share these vital skin cancer prevention tips with your family and friends. The more people who are informed, the safer our communities will be.
Conclusion
Skin cancer prevention is a lifelong journey, but it's one that yields immense rewards: a healthier, more resilient you. By understanding the risks, adopting smart sun protection habits, and staying vigilant with skin checks, you are taking powerful steps to safeguard your health.
Don't wait until it's too late. Make skin health a top priority. Your skin protects you every day; it's time to return the favor. Embrace these skin cancer prevention tips, and enjoy the sun safely!